Contents
🌡️Blood
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you should be able to describe:
- The circulatory system in animals,
- Circulatory mechanisms,
- The components of the circulatory system.
Cool Facts about the Circulatory System
The body of an adult contains blood vessels that can stretch over 60,000 miles when joined end-to-end.
An adult's heart pumps about 4,000 gallons of blood each day.
In one day, the heart beats about one hundred thousand (100,000) times.
Females' heart beat faster than males'.
One drop of blood contains 250 million red blood cells and 275,000 white blood cells.
Human lips have a reddish color because of the concentration of blood capillaries just below the skin. The blood in these capillaries is normally highly oxygenated and quite red. This explains why the lips appear pale when a person is anaemic.
Introduction to Circulatory System
Circulatory System is also called Cardiovascular system.
Some substances are required by the cells of different parts of a multicellular organism for these parts to function properly. Substances like digested food and oxygen are required by every body cells.
However, because of high complexities, the cells of the different parts of the organism's body cannot access these substances (E.g food substances in the small intestine and oxygen in the lungs) unless they are reached to by a transport network. This transport network that conveys important substances to every body part is called the circulatory system.
Circulatory System is a complex connection that works like a transport network and carries important substances (oxygen and nutrients) to every cells and tissues around the entire body.
How does a Circulatory System primarily work
A circulatory system basically works by using blood to move substances around the body via various interconnected blood vessels, ultimately with the use of a pump!
A Circulatory System or cardiovascular system comprise of more than 60,000 miles of BLOOD VESSELS (may be less for smaller animals and more for bigger animals) with a PUMP that beats about 100,000 times a day.
General Functions of the circulatory system
A Circulatory System performs three principal functions:
- Transport
- Homeostasis
- Protection
Transport Functions
• The circulatory system picks up food and oxygen from digestive and respiratory systems and deliver them to cells.
• The circulatory system picks up carbon(IV)oxide and wastes from cells and deliver them to the lungs and kidneys.
• The circulatory system transports hormones, enzymes and other chemical substances throughout the body.
Homeostasis Functions
• The circulatory system maintains Acid/base Concentration in the cells and tissues.
• The circulatory system transfers excess heat from cells to skin for removal.
• The circulatory system maintains fluid and electrolyte balance in tissues and cells.
Protection Function
• Some cells and chemicals that are conveyed by the circulatory system actively seek out pathogens and remove them from the body (technically referred to as lymphatic system and will be discussed in subsequent chapters).
Circulatory Systems in the various Phyla of the Animal Kingdom
While circulatory system consist of a complex transport network, it varies in the different Phyla of the Animal Kingdom. Some organisms have no circulatory system. Others have an open circulatory system while the most complex animals have a closed circulatory system.
No circulatory system
These organisms technically have no transport system. Their body structure is so simple that important body substances travel to every cells through diffusion. Wastes are also collected without any hassle. Examples of those organisms are the first four phyla in the Animal Kingdom:
- Porifera
- Cnidarians
- Platyhelminthes
- Nematoda
Open circulatory system
In an open circulatory system, blood is pumped by a heart (the pump) into the body cavities, where tissues are.
Let me use this illustration:
In a community, delivery pipes are usually used to convey customers' goods to them. Here in open circulatory system, the delivery pipe (blood vessel) carries goods from the factory (heart) and throws off the goods to an open space where the recipients are. This is because there's no network that leads to the recipient's doorstep.
I hope you got that?
The blood is pumped by the heart into the spaces where the cells and tissues are. The cells will absorb its needed substances and then give out its own waste and pass it back to the heart for renewal and disposal.
As a result, the blood flow in an open circulatory system is always slow.
The phyla that make use of the open circulatory system are:
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca (except squids and octopuses)
- Echinodermata
- Chordata (tunicates)
Closed circulatory system
In a closed circulatory system, blood is pumped by a heart into vessels which carry it around the several cells of the body. The wastes from these cells are collected through these vessels and carried back to the heart for recycling and disposal. Hence, the whole process is a cycle through vessels.
Using my previous illustration of the delivery pipe, in closed circulatory system, the delivery pipe runs through every recipient's house. It also collects their waste and conveys them back to the factory for recycling or disposal.
I believe you also got that?
In closed circulatory system, there's usually no blood in the body cavities (blood only passes through blood vessels) and the resulting blood flow is fast.
The phyla that make use of the closed circulatory system are:
- Annelida
- Mollusca (squids and octopus)
- Chordata (cephalochordates and vertebrates)
Components of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system is composed of:
- Heart — The pump
- Blood — Carrier of substances
- Blood vessels — Pipes through which blood travel
- Lung — Blood oxygenator
Pathways of Blood flow (Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation)
Blood flows through 2 major pathways in the body. These pathways are:
- Pulmonary circulation
- Systemic circulation
Pulmonary circulation
PRO TIP: If you see pulmonary anywhere in Anatomy, you should know that what we are talking about is lung related
Pulmonary circulation is a kind of circulation that deals with the lungs in mammals and gills in fish.
The Lung is an organ which its major function is to exchange oxygen and carbon(IV)oxide with the environment. It usually occur in pair. These lungs have small sacs which absorb oxygen.
These small sacs are called alveoli (singular: alveolus).
When oxygen gets to these microscopic sacs via the respiratory system, there's no next thing to do, until the circulatory system comes to take the oxygen from the alveoli (through the use of blood) which will then be carried to the heart for it to be pumped around the body.
Therefore, the pulmonary circulation is the circulation that is directly connected with the oxygenation of blood.
It consists of a short loop that carries deoxygenated blood (=blood which its oxygen is exhausted) to the lungs where it is converted to oxygenated blood (=blood with rich oxyen) which is now carried back to the pump (heart).
Systemic Circulation
This is a type of circulation that takes place after pulmonary circulation.
Blood from the pulmonary circulation (or pulmonary circuit) is conveyed back to the heart, which now pumps it around the entire body.
The circulation of blood between the heart and the different parts of the body is referred to as the systemic circulation.
Systemic circuit carries blood from the heart to different body tissues, and also conveys blood back to the heart.
I believe that by now, you can explain pulmonary circulation and Systemic Circulation if I asked you to.
Let me childishly explain how these two work together:
Blood is the carrier of substances around the body.
Body cells require substances like oxygen, but there is no way they can get it.
Therefore Blood needs to get that oxygen which body requires.
Blood needs to travel along its first path basically to go get oxygen.
The first path is the collection path.
Blood is pumped by the heart into the lungs.
Lungs have oxygen.
Lungs transfer oxygen to Blood.
Blood has collected what the body needs (oxygen).
Blood becomes Rich Blood.
But Rich Blood cannot move from the lungs straight around the body.
This is because Rich Blood might just stop along the way (an exception is in smaller animals).
So Rich Blood needs to be pumped by a pumping machine which is the heart.
Rich Blood finds another way to return from the lungs, back into the heart (completing a pulmonary circulation).
The heart (pumping machine) then pumps out Rich Blood into blood vessels with force!
Rich Blood can now move freely around the body.
As Rich Blood travels through the body, it gradually begins to lose its oxygen to the body tissues.
At the end of the day, there will be no oxygen left in Rich Blood.
Rich Blood becomes Poor Blood.
Poor Blood then passes through another set of vessels that will take it back to the heart (completing a systemic circuit).
Poor Blood reaches the heart.
Heart pumps Poor Blood to the Lungs.
Lungs supply Poor Blood with oxygen.
Poor Blood becomes Rich Blood again!
Rich Blood returns to the heart, and is again pumped around the body, Rich Blood loses its oxygen to body cells, and become Poor Blood which will return to the heart and repeat the process.
Now, you see the entire process is nothing but a cycle.
Rich Blood is known as oxygenated blood; it is oxygen-rich.
Poor Blood is known as known as deoxygenated blood; it is oxygen-poor.
The Heart (The Pump)
We are more aware of our heart than most other internal organs.
Some ancient Chinese, Egyptian, Greek and Roman scholars correctly believed that the heart is a pump for filling vessels with blood.
Aristotle however thought the heart was the seat of emotion and a source of heat to aid digestion. His thoughts predominated for over 2000 years before its true nature reemerged.
The heart is one of first organ systems to appear in developing embryo. By the 4th week of a foetus' development, the heart is already beating.
The study of the heart is known as cardiology, which we are going to be doing little of it right now.
Many people call the heart a crazy machine! No machine works as long or as hard as the heart.
The heart beats about 100,000 times a day at a base level. If an animal goes through stress or activities, it usually beats more than that.
I calculated this times 365 days in a year, that sums up to around more than 35 million times each year.
Structure of the heart
The heart is basically a muscle that contracts (tightens together) to pump blood.
The human heart takes the size and shape of a closed fist. Close your fist together, you will see approximately how big your heart is.
The heart is enclosed within its own sac (called pericardium or parietal pericardium). This is the outer membrane that covers the heart.
The layer before the pericardium is the epicardium or Visceral pericardium. Epicardium is another membrane that covers the heart, just it is thinner than the
pericardium.
Between the pericardium and the epicardium is the pericardial fluid which performs the major function of lubrication.
PRO TIP: pericarditis is the inflammation of pericardium. Here, the membrane become dry and each heartbeat becomes painful.
The muscular layer or muscle tissues of the heart is known as Myocardium.
The internal lining or membrane inside of the heart and heart valves is known as Endocardium.
PRO TIP: cardi.. refers to the heart. So scientifically, the name of the popular American singer Cardi B is translated as heart B, poor joke.
The functional parts of the heart is made up of several chambers, vessels and valves.
Heart chambers
This is the interior of the heart (like different rooms in a small building).
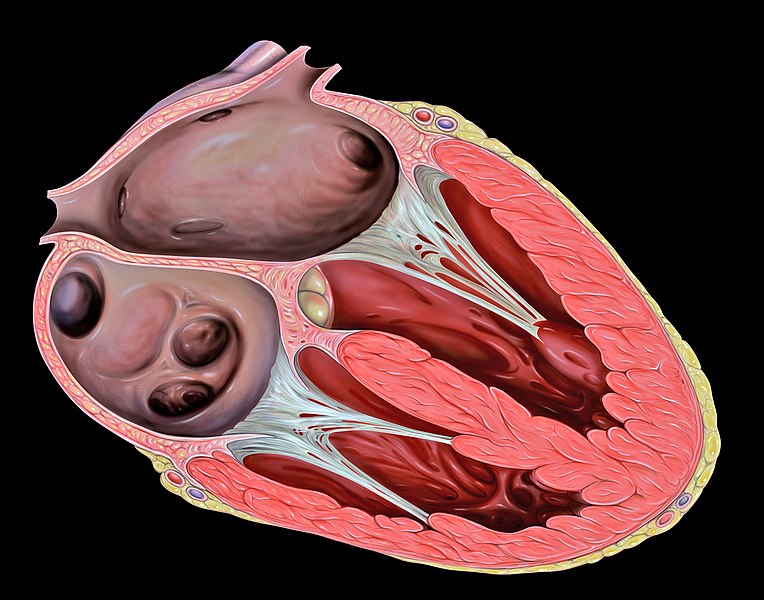
Chambers of a 4 Chambered heart | Photo credit: creativecommons
The chambers of the heart are Auricles (also called atrium / atria) and Ventricles.
Auricle
An auricle, also called atrium (plural: atria) is the chamber of the heart where blood is received from the body.
Auricles are usually thin and they serve as the blood entry point into the heart.
Blood enters the heart through the auricles.
In higher animals, auricles are usually located at the top section of the heart.
Ventricle
Ventricle is the second chamber of the heart beneath the auricles. It is the blood pumping section of the heart.
Ventricles are usually thick and they are responsible for the ejection of blood out of the heart into the great arteries.
Heart chambers vary in different animals
A fish heart for example, has only 2 chambers: one auricle and one ventricle.
Blood is collected into the auricle from the body. The blood passes down to the ventricle which pumps the blood into the gills section.
It is at these gills that the blood get oxygenated.
The blood does not move back into the heart for repump here.
It simply moves through the various cells in the fish and recollect again at the auricle.
This makes it to be said that the circulatory system of fish is unidirectional. Just one pump and the blood moves round.
A frog which is an amphibian; its heart has 3 chambers: two auricles and one ventricle.
Blood is collected from around the body into the first auricle.
The auricle passes down the blood to the ventricle which pumps out the blood into the lungs.
Blood gets oxygenated and returns into the heart via the second auricle for a second pump.
This second auricle passes down oxygenated blood into the same ventricle that was used to pump out deoxygenated blood.
Something now happens which is the mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood.
The ventricle pumps out this mixed blood into the various parts of the frog.
Reptiles also have 3 chambered hearts.
Some operate like that of the frog while some others are upgraded.
Instead of the blood to just mix anyhow in the one ventricle that they have, there's a thin line of tissue that just prevents that. However, the blood still mixes, but not like that of the amphibians.
Crocodiles on the other hand are known to have four chambered heart.
In Birds and mammals, their hearts are 4 chambered.
Two auricles and two ventricles which are separated.
The separation of ventricles is nature's fix to prevent mixing up of oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood.
PRO TIP: the different auricles and diffent ventricles are separated into left and right by a thick line of muscle called septum
PRO TIP: the septum that separates two auricles (atria) from each other is called interatrial septum. The septum that separates two ventricles from each other is called interventricular septum
These auricles and ventricles are separated into right and left by a thick muscle called septum.
Therefore, birds and mammals have right auricle, right ventricle, left auricle, left ventricle.
I want you to use yourself as a picture, as you're sitting or maybe standing while reading this, look at your right hand side and waive your right hand onto your screen, deoxygenated blood is actively entering into the right auricle of your heart from your body.
This blood is passed down into the right ventricle which pumps it out to your lungs for oxygenation (via pulmonary artery).
Oxygenated blood does not return to your heart into the right auricle now again, but through the left auricle.
So on your left hand side, oxygenated blood from your lungs is entering into the left auricle of your heart.
This blood is passed down to the left ventricle of your heart where it is pumped out around your body (via aorta).
Therefore, Systematically, deoxygenated blood operate in the right section of the body, while oxygenated blood operate in the left section of the body.
Blood enters the heart into the auricles, which passes it down into the ventricles where it is pumped out of the heart. To prevent backflow of blood from ventricles, back into the auricles; or backflow of blood into the ventricles after pumping- the heart makes use of valves.
Heart Valves
Valves act as restraining gates to control the direction of blood flow.
Properly functioning valves allow blood to flow only in a forward direction, by blocking it from returning to the previous chamber.
They are situated at each entrances and exits of ventricles.
Blood enter the ventricles from the auricles.
Blood exit the ventricles into the pulmonary artery or aorta.
This means that there are valves between every ventricle - auricle, and also between ventricle - pulmonary artery, and between ventricle - aorta.
The valve between an auricle and a ventricle is called atrioventricular valve.
Since there are two auricles and two ventricles in mammals and birds, this means that there will be two atrioventricular valves right?
The atrioventricular valve between the right auricle and right ventricle (don't forget that deoxygenated blood operate here) is called Tricuspid Valve. Once deoxygenated blood get into the ventricle, it cannot go back up into the auricle again. The prefix, tri– meaning three, indicates that this valve has three leaflets or cusps.
The valve between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery is called Pulmonary valve.
This valve can sometimes be referred to as a SemiLunar valve. The prefix, semi– meaning half, and lunar– meaning moon; joined together means half moon. This indicates that the pulmonary valve appears like a half moon.
On the other hand, the atrioventricular valve between the left auricle and left ventricle (don't forget that oxygenated blood operate here) is called Bicuspid valve or Mitral valve. The prefix Bi– two indicate that the valve has two cusps.
Finally, the valve between the left ventricle and the Aorta is called Aortic valve. Aortic valve is also a SemiLunar valve – looks like half moon.
Heart Vessels
There are 4 major vessels attached to the heart:
2 arteries (they take blood away from heart):
• Pulmonary Artery: carries blood away from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
• Aorta: carries oxygenated blood away from the heart and distribute it to various parts of the body.
2 veins (they bring blood back to heart):
• Vena Cava: Convergence of several veins from the various parts of the body that bring circulated blood to the heart for recycle. There are superior vena cava and inferior vena cava in a Mammalian heart.
• Pulmonary vein: carries newly oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
Blood Flow through the heart
The flow of blood through the heart is very orderly.
It progresses through the heart to the lungs, where it receives oxygen; then goes back to the heart; where it is pumped out to the body tissues and parts.
The normal process of blood flow in mammals is:
Deoxygenated blood from all the tissues in the body enters a relaxed right atrium via two large veins called the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava.
The right atrium contracts and blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the relaxed right ventricle.
The right ventricle then contracts and blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, which carries it to the lungs for oxygenation.
The left atrium receives blood returning to the heart after being oxygenated by the lungs. This blood enters the relaxed left atrium from the four pulmonary veins.
The left atrium contracts and blood flows through the mitral valve into the relaxed left ventricle.
When the left ventricle contracts, the blood is pumped through the aortic valve and into the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The aorta carries blood to all parts of the body.
It can be seen that the heart chambers relax, in order to fill, and contract to push blood forward.
The period of time a chamber is relaxed is diastole.
The contraction phase is systole.
Cardiac Cycle
What happens during a heartbeat?
- Systole: Contraction of each chamber.
- Diastole: Relaxation of each chamber.
Two auricles contract simultaneously. As they relax, ventricles contract.
Contraction and relaxation of ventricles produces characteristic heart sounds:
Lub-Dub (what locals will call gbim gbim!)
Lub = systolic sound (contraction sound)
Here, atrioventricular valves are closing and ventricle is contracting.
Dub = diastolic sound (relaxation sound)
This is a shorter, sharper sound. Here, ventricles relax and SemiLunar valves close.
The characteristics heartbeat sound is as a result of the closing of the atrioventricular valves and the SemiLunar valves.
In other words, a "heartbeat" is really the sound of the valves in the heart closing as they push blood through its chambers.
Conduction system of the heart
Contraction and relaxation of auricles and ventricles are aided by Cardiac muscles.
Cardiac muscle cells are not individually controlled like skeletal muscle cells. They are self stimulating.
This is because the heart beat is regulated by the autonomic nervous system; therefore, there is no voluntary control over the beating of the heart. If you can control your heart when to stop beating or start beating let me know in the comments so I can come knock your head!
The Cardiac muscle cells cause a rhythmic beating of the heart and is coordinated and maintained by special tissues within the heart, responsible for conducting an electrical impulse to stimulate the different chambers to contract and relax in the correct order.
This conducting system or special tissues consists of:
1. Sinoatrial node
2. Atrioventricular node
3. Atrioventricular Bundle (Bundle of His)
• The Sinoatrial (SA, S-A) node, or pacemaker, is where the electrical impulses begin.
• From the sinoatrial node, a wave of electricity travels through the auricles, causing them to contract, or go into systole.
• When auricles contract, the Atrioventricular node is stimulated.
• This AV node transfers the stimulation wave to the Atrioventricular bundle (formerly called Bundle of His).
• The electrical signal then travels down and move through the 2 branches that are within the interventricular septum (muscle between the two ventricles).
• The Purkinje fibers which are situated in the ventricular muscles are stimulated, resulting in ventricles contraction or ventricular systole.


The heartbeat conducting system. Sinoatrial node is seen projecting the first wave in (2). In (3) the atria are contracted. In (4) the wave is picked up by atrioventricular node, passes through the atrioventricular Bundle until it gets to the Purkinje fibers. In (5) and (6) the ventricles are contracted. The process then repeats.
You see the trend?
Sinoatrial node > Atrioventricular node > Atrioventricular Bundle > Purkinje Fibers.
Sinoatrial node releases electricity that makes the auricles to contract. The contraction effect releases a wave is then relayed to the Purkinje fibers, which finally makes the ventricles to contract too.
By the time the waves reach the Purkinje fibers, the auricles have become relaxed.
The auricles and ventricles cannot contract at the same time. This will lead to a big issue.
While the auricles contract, the ventricles are relaxed and when the auricles relax, the ventricles can then contract.
When ventricles relax, sinoatrial node sends in another wave of electrical impulse.
Watch the first video in the Recommended Videos section if you do not get this
explanation.
If I ask you to explain the mechanism of a functioning heart for me, can you?
Don't tell me No! If your answer is no, go back up and read this post right from the beginning again. If you're following me, then let's ride on!
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
The heart conducting system generates a small electrical current that can be picked up by an electrocardiograph.
Electrocardiogram, commonly referred to as an EKG or ECG, is a measurement of the electrical activity of the heart.
This can give the physician information about the health of the heart.
That heartbeat reading that you usually see in hospitals, that goes like a wave reading, that is an example of an electrocardiogram.
It goes up down, up down just as you can see in this image.
You should know that ECG is not a record of heart contraction, it is a record of the electrical activity of the heart. Many usually get that minced.
Blood (Carrier of Substances)
The Blood is primarily a mixture of several substances: these substances are Plasma, dissolved nutrients and cellular components.
45% to 50% composition of blood is Red Blood Cells.
Roughly 50 to 55 % composition of blood is plasma.
Plasma is the liquid-only portion in which cellular components are distributed.
Plasma contains 90% water with dissolved substances such as glucose (blood sugar), hormones, enzymes, and also waste products such as urea and lactic acid.
Plasma acts as a buffer (neutralizes acids and bases) maintaining pH near 7.4.
Plasma also contains proteins such as albumin, fibrinogen (important in clotting), and globular proteins or globulins.
Asides the plasma, there are 3 important components of the blood:
- Red Blood cells (Erythrocytes)
- White Blood cells (Leukocytes)
- Platelets
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Red blood cells shape is described as Bio-Concave (or disc-shaped) as they have depressions on both sides, this makes them to have a maximum amount of surface area to absorb oxygen from the lungs.
Red Blood cells are the Transporters of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide in the blood.
Red Blood Cells Lack nucleus.
Red blood cells contain an iron pigment called haemoglobin which gives them their characteristic red colour when oxygenated.
Red blood cells are produced in red bone marrow of the:
- Ribs.
- Humerus (upper arm bone).
- Femur (upper leg bone).
- Sternum, and other long bones.
Red blood cells live for about 120 days.
Once a red blood cell completes its lifespan, it is destroyed in the liver or spleen.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
White blood cells defend against disease by recognizing proteins that do not belong to the body.
They are made from stem cells in bone marrow.
There are five types of leukocytes which are important components of the immune system.
• Neutrophils – react against bacterial and fungal infections.
• Monocytes – react against bacterial infections.
• Eosinophils – react against parasitic infections.
• Basophils – responsible for responses to allergens.
• Lymphocytes – react against viral infections.
White blood cells are able to ooze through the walls of capillaries to move round the tissues and reach the lymphatic system.
Read more on white blood cells on: https://teachmephysiology.com/immune-system/cells-immune-system/white-blood-cells/
Platelets
Platelets are cell fragments used in blood clotting.
They are derived from fragments of megakaryocytes.
Platelets also lack nucleus and they usually have a short lifespan, usually about 10 days.
Humans or animals with insufficient platelet cannot clot wounds, they are referred to as haemophiliacs.
Extraneous Tip: Do you find that mosquitoes and other biting insects choose you, rather than other people?
Did you ever wonder why?
If you have Type O blood, they prefer you twice as much, than others, who have Type A !! People with Type B, fall in the middle of these 2.
An estimated 20 percent of people are especially delicious for mosquitoes, and get bit more often on a consistent basis.
Blood Vessels (Pipes through which blood travel)
Blood vessels are pipes that circulate blood throughout the body. The Lumen is the channel within these vessels through which blood flows.
There are 3 major blood vessels:
- Arteries
- Capillaries
- Vein
Arteries
The arteries are large, thick-walled vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
I do recall this by:
A - rteries
A - way
Both words start with the letter A. So if you say arteries, I will remember A also stands for away, so we are talking about vessel that carries blood Away from the heart to other parts of the body.
The arteries are usually elastic, large and thick-walled.
The arteries transport blood under very high pressure.
The walls of arteries contain 3 thick layer of smooth muscle that can contract or relax to change the size of the arterial lumen (lumen is the space or hole through which blood travel).
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
The largest artery (aorta) carries oxygenated blood to all the body systems.
The coronary arteries branch from the aorta and provide blood to the muscles of the heart itself.
As arteries travel through the body, they branch into progressively smaller-sized arteries.
The smallest of the arteries, called arterioles, deliver blood to the capillaries.
Capillaries
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that collect blood from the arterioles.
They are responsible for the exchange of substances between the blood and tissues.
They usually weave together and form a called Capillary bed.
Blood coming from arteries flow through capillary bed.
Capillaries are usually very thin walled (about one cell thick) and the internal diameter for blood flow is small. This makes diffusion very easily done. Substances are exchanged between the blood and tissues via the capillaries.
Since the capillaries are very small in diameter, the blood will not flow quickly through them as it does through the arteries and veins. This means that the blood has time for exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste material to take place.
As blood exits a capillary bed, it returns to the heart via veins.
Vein
Veins carry blood back to the heart.
When blood leaves the capillaries, it first enters small venules (small veins).
Small venules collect together to form a larger vein.
The walls of veins are very much thinner than arteries. This makes it that whenever a vein is not filled with blood, it collapses.
Veins have valves that allow blood to move only toward the heart.
Several veins collect together to form Vena Cava (very large veins) that actually carry blood into the right auricle of the heart.
Vena cava are of two types:
Superior Vena Cava which carries blood from the upper part of the body into the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava which carries blood from the lower part of the body into the heart.
There's much lesser blood pressure in veins compared to the high blood pressure in the arteries.
Walls of Blood Vessels
The walls of arteries and veins consist of three layers:
- Tunica Externa
- Tunica Media
- Tunica Interna
Tunica Externa
Tunica externa, also called Tunica adventitia is the outer connective tissue of the blood vessels. It anchors the arteries and veins and provide passage for small nerves, lymphatic vessels and smaller blood vessels.
Tunica Media
Tunica media is middle section of the vessels' walls and it is made mainly of smooth muscle with some elastic tissue and collagen fibers.
Tunica media strengthens vessel walls and make them able to withstand high pressure.
Tunica media is also responsible for the dilation and constriction of blood vessels and it is usually the thickest layer, especially in arteries (arteries are thickest blood vessels).
Tunica Interna
Tunica interna or Tunica intima is the innermost part of the vessels'walls. It is the portion of the wall that is exposed to blood (also called endothelium).
PRO TIP: when blood vessels contract, it is called vasoconstriction; but when they relax, it is called vasodilation.
Special Circulation Patterns
Coronary Circulation (or Cardiac Circulation)
The heart itself needs an abundant supply of oxygen and nutrients just like every other organ in the body.
The heart's muscles (Myocardium) has its own supply of vessels.
5% of blood goes to heart muscle tissue. Any interruption of blood flow can cause necrosis within minutes.
Blood is supplied to the heart muscle by the Coronary arteries.
The coronary arteries branch into right and left and they originate from the aorta (major artery that carries blood out of the heart).
However, there's something that happen in the coronary arteries:
Blood enter the coronary arteries when the ventricles relax (most vessels receive blood when ventricles contract).
After going through the heart's muscles, the blood returns back to the heart through veins that drain into coronary sinus, which then empties into Right auricles.
Circle of Willis
Circle of Willis are 7 separate arteries that branch from the internal carotids (artery that carry blood to the brain) and vertebral arteries.
An Arterial anastomosis interconnects the arteries to form a circle of connecting arteries, at the base of the brain. This results in more than one route for blood to get to brain.
Hepatic Portal System
The veins from spleen, stomach, pancreas, gall bladder, and intestines merge to form the hepatic portal vein.
Hepatic portal vein does not take blood directly to Vena Cava like all other veins in the body.
Hepatic portal vein takes blood to the liver for "inspection".
Phagocytic cells remove toxins from the blood in liver.
Blood pressure and Pulse
Blood Pressure is the force of the blood flowing through blood vessels.
Blood pressure is measured in mmHg (millimetres of mecury).
Changes in pressure (or pressure gradient) are the driving force that moves blood through the circulatory system.
The pulse which is felt at the wrist or throat is the surge of blood caused by the heart contraction. This is why pulse rate is normally equal to heart rate.
Blood pressure is created by:
- The force of the heart beat. The heart maintains a high pressure on the arterial end of the circuit.
Measuring Blood Pressure
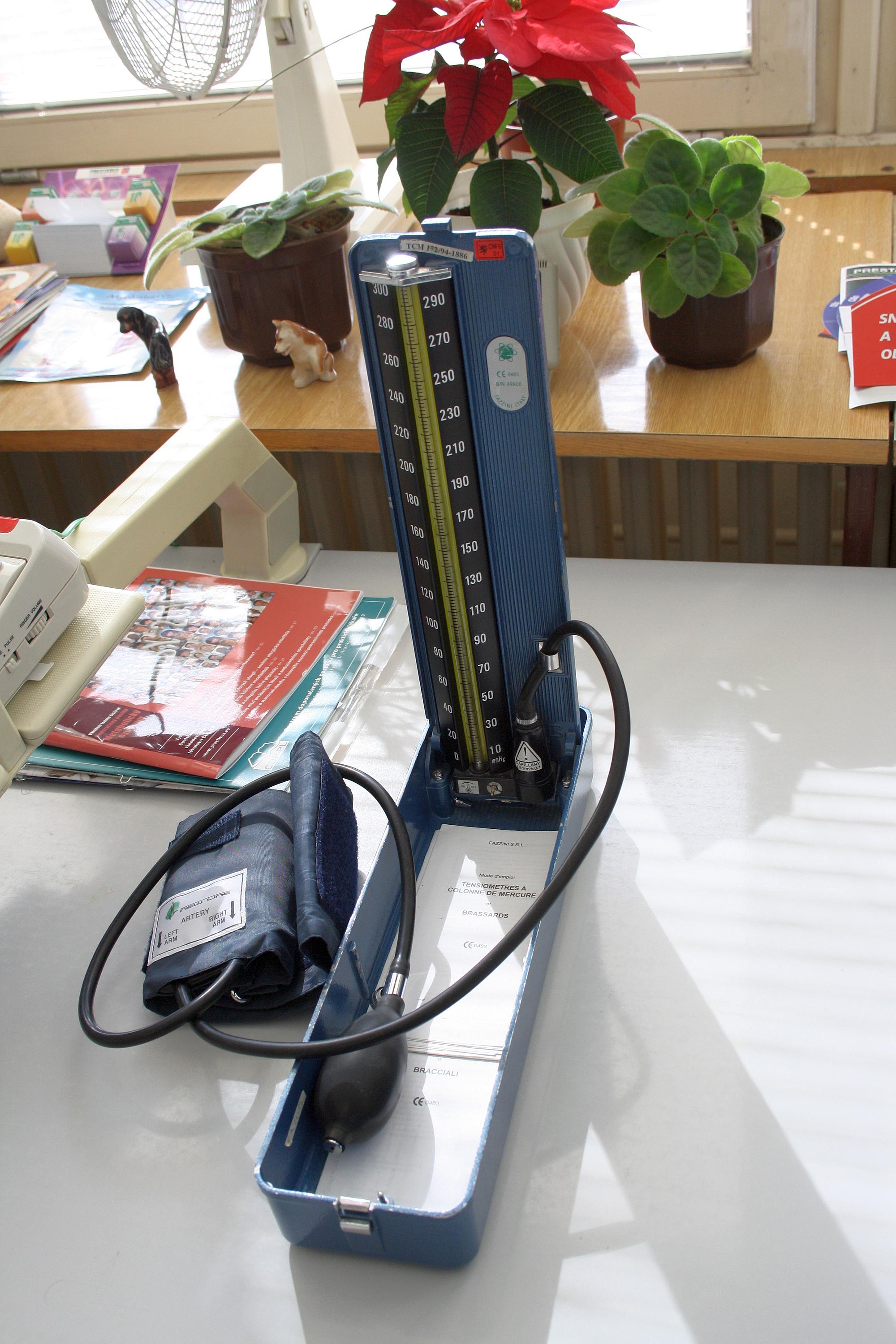
Blood pressure is measured with the use of a sphygmomanometer.
It is usually used to measure blood pressure in the brachial artery (located in the biceps).
A Normal Blood Pressure (normal BP) should read around 120/80
Normal Blood Pressure range is: 110-140 / 75-80 [mm Hg]
The numerator (120) is the systolic pressure which is the force of ventricles contraction.
The denominator (80) is the diastolic pressure which is the resistance of blood flow.
Diseases of the Circulatory System
• Arrythmia (dysrrhythmia): any change from normal heart rate or rhythm.
• Bradycardia: slow heart rate of less than 60 pulse per minute.
• Tachycardia: rapid heart rate of greater than 100 pulse per minute.
• Angina pectoris: chest pain due to the lack of oxygen to heart muscle, usually treated with nitroglycerine.
• Edema: venous congestion; heart failure can cause poor circulation that results in edema.
• Hypertension: High blood pressure: over 140/90, called the silent killer because there are usually no symptoms.
• Hypotension: low blood pressure, patient or animal becomes dizzy especially when standing up suddenly.
• Embolism: traveling blood clot
• Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
• Cerebral vascular accident in humans (CVA) stroke.
• Varicose veins: swollen, enlarged veins result from a slowing of blood flow back to the heart.
• Aneurysm: abnormal condition, ballooning or protrusion of the wall of an artery.
• Arteriosclerosis: arterial walls thicken and lose elasticity.
• Atherosclerosis: fatty deposits form on walls of arteries and block circulation, reducing the amount of blood going to an organ.
• Heart attack: heart attack begins with the buildup of plaque in the arterial wall, white blood cells come to solve the issue, but then the case is worsened.
• Hypertrophy: stressing of the heart by pressure overload.
Haemoglobin measurement
The amount of haemoglobin in the blood of an animal is expressed in grams per deciliter (g/dl).
The normal haemoglobin level for males is 14 to 18 g/dl.
The haemoglobin level for females is 12 to 16 g/dl.
When haemoglobin level is low, the patient is said to have anaemia (lack of haemoglobin pigmentation in the blood).
Erythropoiesis
Haematopoiesis is the formation of all blood components.
Erythropoiesis is a process that is concerned with the production of red blood cells.
An erythropoietic stem cell develops to form a mature red blood cell in the red bone marrow of bones.
Erythropoietin is a hormone, produced by the kidney, and it stimulates the production of red blood cells in the red bone marrow.
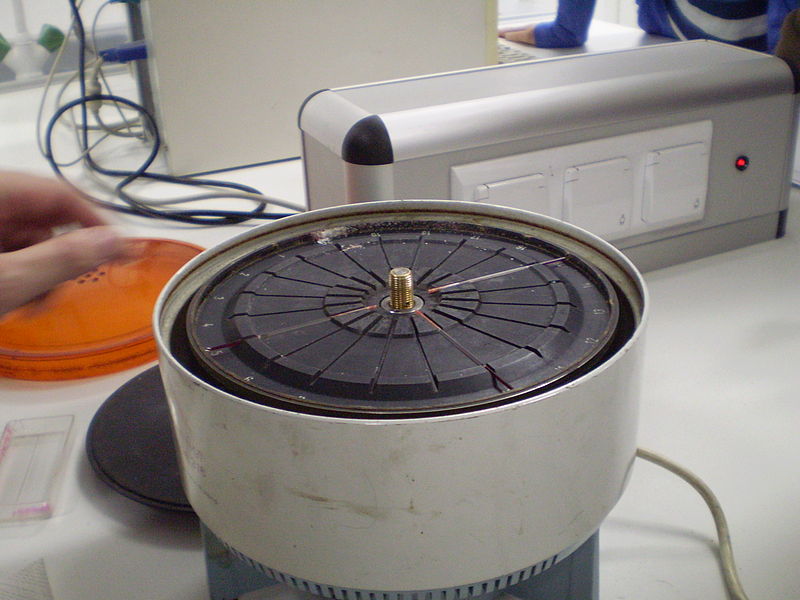
Haematocrit Test
A haematocrit test, also known as a packed cell volume test (PCV test) or erythrocyte volume fraction (EVF) is a simple blood test that employs the use of a centrifuge (fast rotating machine that separates the constituents of a mixture inside a test tube) to measure the proportion of erythrocytes or red blood cells in an animal's blood.
It is different from haemoglobin measurement in the sense that haemoglobin measurement deals with the proportionate mass of haemoglobin in the blood.
Measurement of haematocrit (Hct) or packed cell volume (PCV) is the most accurate and simplest of all tests for detecting the presence and degree of anaemia or polycythaemia. In comparison, haemoglobin estimation is less accurate, and Red Blood cells count are far less accurate.
After centrifugation has been carried out, blood is separated into its constituents which are red blood cell fraction, white blood cell fraction and plasma.
The percentage of red blood cell is then calculated using simple arithmetic:
%RBC (PCV) =
× 100%
The height of the white blood cells can be negligible.
The normal values of PCV vary according to the age and sex of the individuals.
The normal ranges are:
- Males: 40 %–54 %
- Females: 36 %–47 %
- Newborns: 55-68 %.
A lower than normal value in an haematocrit test indicate:
• An insufficient production of healthy red blood cells which is as a result of anaemia.
• Vitamin or mineral inadequacy and deficiency.
Blood has been lost either not too long before the test or long term blood loss.
• Acute kidney disease (this leads to lower Erythropoietin production. Lower Erythropoietin leads to less RBC production in the bone marrow).
• Pregnancy may lead to women having additional fluid in blood. This could potentially lead to a small drop in haematocrit levels.
PRO TIP: when a large number of white blood cells is discovered in the blood (than it is normal) this could be due to long-term illness, infection, leukemia, lymphoma or other disorders of white blood cells.
A higher than normal haematocrit may indicate:
• Abnormal increase in red blood cells.
• A disorder, such as polycythemia vera that causes an organism's body to produce too many red blood cells (in polycythaemia it may rise to as high as 70 %).
• At higher altitudes, there is a lower oxygen supply in the air and thus haematocrit levels may increase over time.
• Low blood oxygen levels (hypoxia).
• Lung or heart disease — if the body senses low oxygen levels, hormonal action will make red bone marrow to produce more red blood cells in an effort to increase the amount of oxygen in the blood.
• Extended Dehydration.
• Burn( due to loss of plasma).
Blood doping
Some athlethes, just before an important competition, withdraw some significant amount of blood from their bodies. When they do this, the blood quickly produces more Red Blood Cells (RBCs) to counter the effect of blood loss.
After sometime, the athlethes reinject their withdrawn blood just before the game. This is because more Red blood cells will lead to more oxygen retention in the body. This is referred to as blood doping.
For further reading on circulatory or cardiovascular system, go to: https://pressbooks.ccconline.org/bio106/chapter/cardiovascular-levels-of-organization/
Summary
☑️The circulatory system also called Cardiovascular system is a system that is involved with the transportation of important substances and nutrients throughout the body of an organism.
☑️A circulatory system basically works by using blood to move substances around the body via various interconnected blood vessels, ultimately with the use of a pump!
☑️General Functions of the circulatory system are:
- Transport of digested food and gases round the cells.
- Maintainance of a constant pH within the body.
- Patrols protective cells which fight foreign cells within the body.
☑️There are 2 types of circulatory systems:
- Open circulatory system
- Closed circulatory system
☑️In open circulatory system, blood vessels do not pass through tissues but is pumped into cavities where tissue can absorb the amount they require.
☑️In closed circulatory system, specialized blood vessels carry blood around each tissue where absorption of important nutrients will take place.
☑️Blood circulation occur in two phases
Pulmonary circulation: process of conveying venous blood (or deoxygenated blood) to and fro the heart basically for oxygenation.
Systemic circulation: process of conveying oxygenated blood around the entire body.
☑️The circulatory system is composed of:
- The heart
- Blood
- Blood vessels
☑️The heart is a muscular pump that does the function of pumping blood.
☑️Hearts have a variety of forms: chambered hearts in mollusks and vertebrates, tubular hearts of arthropods, and aortic arches of annelids.
☑️Accessory hearts are used by insects to boost or supplement the main heart's actions.
☑️Fish, reptiles, and amphibians have lymph hearts that help pump lymph back into veins.
☑️The heart has important chambers:
- Auricles or atria
- Ventricle
☑️Blood enters the heart through auricles and is pumped via ventricles.
☑️Valves are used by the heart to prevent backflow of blood from one chamber or artery to another.
☑️In higher animals (with 4 chambered hearts), the valves are:
- Two atrioventricular valves known as Bicuspid and tricuspid valves.
- Two SemiLunar valves.
☑️The heart has 4 important blood vessels
- Aorta (largest artery)
- Pulmonary trunk (or pulmonary artery)
- Pulmonary vein
- Vena Cava
☑️Contraction of the heart's muscles is called systole.
☑️Relaxation of the heart's muscles is called diastole.
☑️Systole + diastole = one cardiac cycle or a complete heartbeat.
☑️Electrical impulses from the autonomic nervous system coordinate heartbeat rhythm.
☑️Electrical impulses are generated in the sinoatrial node which stimulates atria to contract. The waves is relayed to the Purkinje fibers present on the myocardium of the ventricles which also makes the ventricles to contract.
☑️Sinoatrial node > atrioventricular node > atrioventricular Bundle fibers > Purkinje fibers
☑️Electrocardiogram (ECG, EKG) measures the electrical activity of the heart.
☑️Blood is composed of:
- Plasma
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
- Platelets
☑️The blood vessels are pipes that carry blood around the body and there are 3 major blood vessels:
- Arteries: carry blood away from the heart. All arteries carry oxygenated blood except the pulmonary artery.
- Capillaries: capillaries form a network of capillary bed and they serve as exchange sites between the circulatory system and tissues.
- Veins: carry used blood back to the heart for recycle. All veins carry deoxygenated blood except pulmonary vein.
☑️Arteries and veins are 3 layers thick.
☑️Capillaries are 1 layer thick.
☑️Coronary arteries serve the heart's muscle cells or myocardium.
☑️All arteries except the pulmonary artery originate from the largest artery (aorta) and divide into smaller arteries called arterioles.
☑️Arteries carry blood with high pressure generated by the heartbeat.
☑️Veins collect from smaller venules. All veins from the body join up at the vena cava except the hepatic portal vein.
☑️Animals often have a portal system, which begins and ends in capillaries, such as between the digestive tract and the liver.
☑️A normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg
☑️A higher reading indicates hypertension and a lower reading indicates hypotension.
☑️Erythropoiesis is the formation of new RBCs with the use of Erythropoietin - a hormone produced from kidney.
☑️Haemoglobin measurement or a haematocrit test is usually used to measure the amount of RBCs in an animal's blood.







































_diagram_en.png)









![GROUP 1A ELEMENTS [ALKALI METALS]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiTaRno3-Kj3zqgfpG848vTTt_gRDTSXvEBS97SXDiXfdr0kAAqk0taqzZFjiAMw8TLF08fqqa2CKsA70_C91Gzk9-P0YHyl8wcJfkqwtyUROMLCGmLf3GSw7c6xMFGUu9x1w8XtPemj-q662_6UoTCZOXna8YZkLzlpZVJHKer-p1EvF9eKLFNZf5pUg/w74-h74-p-k-no-nu/Group%201A%20elements%20Alkali%20metals.jpg)



