Contents
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you should be able to:
- Describe the endocrine system.
- Describe the classes of hormones.
- Explain the major glands of the endocrine system.
Introduction
In previous posts, we have discussed several systems that make up a multicellular organism. Various parts and organs of every animal communicate with one another to ensure that a constant internal environment (i.e homeostasis) is maintained. Communication amongst various regions of the body is also essential for enabling an animal to respond to any change in its internal and external environments. There are two systems that help to ensure communication between various organs in the body: The nervous system and the hormonal system.
Nervous system exerts rapid controls while Hormonal system exerts more prolonged effects.
Nervous system uses electrical signals (called impulses) and chemical signals (called neurotransmitters) to communicate between several organs of the body, whereas the Hormonal system makes use of chemicals (called hormones).
You can read more on nervous system here
What is Endocrine System?
The Endocrine system includes all organs and tissues that produce and secrete hormones, which are used by the body to regulate and coordinate all the vital body functions like growth and development, metabolism, sexual function and reproduction, sleep and mood.
What is a gland?
Organs and tissues which their primary functions are production and secretion of hormones, are called glands.
Exocrine glands and Endocrine glands
Exocrine glands are those organs and tissues that release hormones into ducts (transport vessels) which convey chemicals (hormones) to the organ(s) where they are to be used (target tissue or receptors).
On the other hand, Endocrine glands are those glands and tissues that do not release hormones into ducts, they release hormones directly to where they are needed, or into the bloodstream, through which the hormones travel, reach and act on the receptor tissue or organ.
Do you see the difference between the two? Exocrine glands release hormones into ducts while endocrine glands do not.
PRO TIP: Local chemical messengers, not generally considered as part of the endocrine system, include autocrines (secrete autacoids) which act on the cells that secrete them; and paracrines (secrete eicosanoids) which act on a different cell that is nearby
Hormones
Hormones are chemicals (or chemical messengers) which are released by glands; they affect the functioning of other cells or tissues.
The function of hormones is to alter (change) cell activity by stimulating (arousing, encouraging, promoting) or inhibiting (discouraging, stopping, blocking) characteristic cellular processes (functions) of their target cells.
Classes of Hormones
There are 3 major classes of Hormones:
- Peptide hormones
- Steroid hormones
- Amino acid-derived hormones
Peptide hormones
Peptide hormones are the largest and most relatively heavy hormones. They are composed of proteins (chains of amino acids of different lengths).
They cannot penetrate the plasma membrane of their target cells (I used to think it is because of their largeness in size, but there's more to it). Peptide hormones tend to exert their effects by binding to receptors on the surface of the plasma membranes of their target cells. This triggers a variety of events, leading to the production of second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP), which, subsequently, initiate the desired effect of the hormone in the target cell.
Some peptide hormones are initially produced as inactive forms, called prohormones;
A good example is insulin, which is usually first synthesised as a much larger molecule, called proinsulin, and then cleaves (divides) into its active, shorter form before being released into the blood.
Examples of Peptide hormones are:
- Somatotropin (hormone that causes an animal to grow)
- Insulin (hormone that converts excess glucose in animals' blood into an inactive form)
- Ghrelin (hormone that makes an animal to feel hungry)
And so many others you will learn them in higher classes.
Steroid hormones
Steroid hormones are lipids (fats), mostly gotten directly from cholesterol (heavy fatty compound).
If you can recall, back in ANP 101, we discussed that every animal cell's plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, this makes steroid hormones to be able to penetrate the plasma membrane of their target cells, and exert their effect by binding to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus.
So if a lecturer asks that why can a steroid hormone penetrate into a cell? you should be able to give a very good answer.
Another thing you need to know is that, steroid hormones (unlike peptide hormones) tend to cajole their target cell into carrying out their desired effect by modulating the activity of particular genes inside the cell. You will learn more on this in higher classes.
Steroid hormones penetrate plasma membrane of their target cells
Examples of Steroid hormones are:
- Oestrogen (hormone that controls sexual and reproductive function in females)
- Progesterone (hormone that controls pregnancy and sexual related functions in females)
- Testosterone (hormone that controls sexual function in males)
- Cortisol (stress hormone, has other functions)
Amino acid-derived hormones
As the name goes, these hormones are gotten from amino acids, which makes them to appear small.
Just like peptide hormones, AAD hormones bind to receptors on their target cell's plasma membrane. However, a few known AAD hormones, like thyroxine T3 from the thyroid, can penetrate the plasma membrane of their target cells.
Examples of Amino Acid Derived hormones are:
- Adrenaline [Epinephrine, derived from an amino acid called thyrosine] (hormone that makes you run when a Bulldog starts running towards you)
- Melatonin [derived from an amino acid called tryptophan] (hormone that makes you feel sleepy, which you may be feeling right now - lazy student, better wake up!!)
Glycoproteins and Prostaglandins
Prostaglandins are lipid–like substances which are modified from fatty acids (arachidonic acid) and have hormone-like properties. They are a group of lipids made at sites of tissue damage or infection that resulted in injury and illness. They control processes such as inflammation, blood flow, the formation of blood clots, contraction of the walls of the uterus in females, and assist in defense mechanisms. Prostaglandins act on nearby cells from where they are produced, and they are destroyed before they reach the bloodstream.
Glycoproteins or G-proteins are protein molecules that have carbohydrate molecule attached to them. They act as messengers when a peptide hormone binds to an hormone receptor. G-proteins activate hormonal response inside a cell.
Negative and Positive Feedback Loop
These are mechanisms that control the level of production of hormones in an animal's body. They let a gland determine when to start producing or stop producing an hormone.
In Negative feedback loop, presence of a stimulus will lead to the production or release of a hormone, when the hormone reaches a particular level, or there's absence of the stimulus, this will lead to a stop in the production or release of the hormone. A popular example is when a male animal sees a female animal on heat, hormonal release in the male animal's body will make it proceed to the female. But once the hormone level reaches a certain point, or the female leaves, the gland that is releasing the hormone will stop its release, which will make the male animal to return to its normal state. That is called negative feedback loop.
On the other hand, in positive feedback loop, presence of a stimulus leads to continuous production or release of hormone. It reinforces stimulus, and It is not as common as negative feedback loop. An example is the period of lactation (milk production of a nursing mother) and during childbirth.
Major Glands of the Endocrine System
Nearly all body organs produce hormones, the most active hormone producers are:
- Hypothalamus
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid gland
- Adrenal gland
- Pancreas
- Gonads
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamus is located at the centre of the brain, just beneath the thalamus.
The function of hypothalamus is to synchronize information from the brain, with secretions of hormones, therefore it is the bridge between the nervous system and the endocrine system.
Hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland through: nervous stimulation (of the posterior pituitary) and hormonal secretion to the anterior pituitary.
Neuronal to POSTERIOR PITUITARY
Endocrine to ANTERIOR PITUITARY
Hypothalamus secretes Releasing hormones (which stimulate the production of other hormones) and Inhibiting hormones (which stop the production of other hormones) to the anterior pituitary gland.
The Releasing hormones that are secreted by hypothalamus are:
- Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone [GHRH] (hormone that stimulates the releasing of growth hormone)
- Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone [TRH or TRF] (hormone that stimulates the release of hormones that will stimulate the production of milk) also called Prolactin Releasing Hormone [PRH]
- Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone [GnRH] (hormone that stimulates the release of sexual related hormones)
- Corticotropin Releasing Hormone [CRH] (Hormone that stimulates the release of cortisol)
The inhibiting hormones that are secreted by hypothalamus are:
- Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone [GHIH] (hormone that stops release of growth hormone)
- Dopamine (has many functions)
- Melatonin release-inhibiting Hormone (hormone that stops the release of melatonin)
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary gland is a pea-sized structure that is usually located at the base of the brain, just behind the nasal cavity, where it is protected by the sphenoid bone of the skull (called sella turcica).
Pituitary gland releases nine peptide hormones.
Seven from anterior lobe [front region] (known as adenohypophysis): Called tropic (trope, a turning) hormones because they “turn on” other endocrine glands.
Two from posterior pituitary [back region] (known as neurohypophysis)
All nine hormones bind to receptors on cells' plasma membrane.
Hormones released by the Anterior lobe of the pituitary gland are:
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
• Targets the thyroid gland.
• Stimulates release of thyroid hormones.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
• Targets Adrenal gland.
• Also known as corticotropin.
• Stimulates release of steroid hormones from adrenal cortex.
Gonadotropins
• Regulate activities of the gonads (reproduction related).
Gonadotropins are of two types:
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
In Females
• Promotes ovarian follicle development and (in combination with LH) stimulates secretion of estrogens.
In Males
• Promotes maturation of developing sperm.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
In Females
• Induces ovulation.
• Promotes secretion of estrogen and progesterone.
• Prepares body for possible pregnancy.
In Males
• Stimulates interstitial cells of testes to produce sex hormones (androgens), primarily testosterone.
Growth hormone (GH)
• Targets skeletal and muscle cells.
• Stimulates cell growth and reproduction by accelerating rate of protein synthesis.
Prolactin (PRL)
• Works with other hormones to stimulate mammary gland development.
• During pregnancy and nursing period, stimulates milk production by mammary glands.
Melanocyte Stimulating hormone (MSH)
• Stimulates melanocytes of skin to increase melanin production (gives the skin its pigmentation).
In adult animals, this portion of the anterior lobe is almost nonfunctional.
There's usually no MSH in circulation.
Hormones released by the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland are:
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
• Primary function of ADH is to promote water retention by the kidneys, and decrease urination.
• It also causes vasoconstriction [tightening of blood vessels] (which helps to increase blood pressure).
• Release is inhibited by alcohol. Try drinking alcohol and drink plenty water and see how many times you will have to go to the toilet to urinate.
Oxytocin (OXT)
• Stimulates muscle contraction in wall of uterus.
• Promotes labor and delivery.
• Contraction of myoepithelial cells in the mammary glands which promotes ejection of milk.
• Has unclear functions in sexual activity.
• Circulating levels rise during sexual arousal: stimulates contraction of vas deferens and prostate in males.
Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland is a bilobed (two-lobed) organ that resembles a butterfly or gaming pad in shape.
It wraps around the trachea at the base of the neck.
The thyroid itself has two major populations of endocrine cells:
- Follicular cells – these produce the iodine-containing hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4, also known as thyroxine), which regulates the metabolic rate of almost all the cells in the body. As thyroxine level increases in the blood, so does the rate of cellular respiration.
- Parafollicular cells – these produce the hormone 'calcitonin' (which Lowers blood–calcium levels by activating osteoblasts. Osteoblasts transform excess calcium in the blood to build new bone tissue)
Parathyroid glands
These are four little glands embedded in the back of thyroid gland.
They secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which act antagonistically to calcitonin by raising blood–calcium levels through activation of osteoclasts (which dissolves bone). As bone dissolves, calcium levels in blood increase.
Adrenal glands
These are 2 roughly triangular glands located at the top of the both kidneys.
Adrenal glands have two major regions:
Adrenal cortex (outer region) – this produces steroid hormones:
- Cortisol: stress hormone.
- Aldosterone: regulates the levels of sodium and potassium in the blood.
Adrenal medulla (inner region) – this produces:
- Adrenaline (epinephrine)
- Noradrenaline (norepinephrine)
These are ‘fight-or-flight’ hormones – usually produced when a person is under threat, afraid or excited.
Primary function is to activate the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system and prepare the body for immediate action.
Pancreas
Pancreas is located behind the right side of the stomach.
Pancreas can be said to be both an exocrine and an endocrine gland.
Exocrine in the sense that it secretes digestive enzymes into a duct leading to the small intestine.
Endocrine because it secretes hormones into bloodstream.
The endocrine component of the pancreas is the islet of Langerhans which secretes hormone into the bloodstream.
Here, Alpha cells secrete glucagon, which targets the liver and directs it to break down fat which has been stored, therefore releasing sugar into the blood, blood-sugar level increases as a result.
Beta cells secrete insulin, which also targets the liver, and muscles, directing them to remove excess sugar from the blood and store it as fat, thereby reducing blood-sugar level.
Gonads
Gonads are sexually related structures.
Ovaries in females, Testes in males.
Ovaries
Secrete estrogen and progesterone which regulate females' menstrual cycle, and develop secondary sexual characteristics during puberty in females.
Endometrium in the uterus also secretes a female hormone that makes it that when a fertilized egg binds to it, the menstrual cycle will automatically stop.
Testes
Secrete male steroid hormones such as testosterone.
Testosterone controls development of male characteristics such as sperm development, and secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Other Well known Endocrine glands
Pineal gland
The pineal gland is a small structure which is located in the brain.
It secretes melatonin, which regulates internal clocks and any rhythmic activities.
It plays a large role in sleep and wake cycles.
Thymus
Thymus is a lymphatic system structure located below the thyroid gland.
It secretes thymosin which stimulates production of T-cell (T-lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell) in young animals.
This gland shrinks with age.
Stomach
Stomach is an elastic structure for temporary food storage and protein breakdown.
The lining of the stomach secrete gastrin which stimulates production of gastric juice for activation of enzymes that will breakdown proteins.
Small intestine
Small intestine is where food molecules are broken down to their smallest and absorbable form, and also absorbed into the circulatory system.
You can read more on it in digestive system.
In the small intestine, secretin and cholecystokinin are secreted.
Kidneys
Erythropoietin is a hormone that is secreted in the kidneys. Erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis (production of Red Blood Cells).
Diseases and Disorders of the Endocrine system
- Hyper = secretion of too much hormone.
- Hypo = secretion of insufficient hormone.
- Target cell insensitivity produces symptoms similar to hyposecretion.
Pituitary Gland Disorders:
Pituitary dwarfism = hyposecretion of Growth Hormone.
Gigantism = hypersecretion of Growth Hormone during childhood.
Acromegaly = hypersecretion of Growth Hormone during adulthood. Enlargement of bones and thickened skin.
Diabetes insipidus = hyposecretion of ADH which causes excretion of large amounts of dilute urine which leads to dehydration and thirst.
Thyroid Gland Disorders:
Cretinism = hyposecretion of thyroid hormones during foetal life or infancy.
Myxedema = hypothyroidism during adult years.
Grave's Disease = an autoimmune disease which is the most common form of hyperthyroidism.
Goitre = enlarged thyroid gland causing swelling in neck; caused by deficiency of iodine in diet.
Parathyroid Gland Disorders:
Hypoparathyroidism results in muscle tetany (muscle cramps and contraction).
Hyperparathyroidism produces osteitis fibrosa cystica (or Brown tumor, when there are too many osteoclasts that dissolves bone) which results in demineralization of the bone.
Adrenal Gland Disorders:
Cushing's Syndrome = hypersecretion of cortisol by the adrenal cortex.
Addison's Disease = hyposecretion of glucocorticoids and aldosterone.
Tumors of the adrenal medulla can cause hypersecretion of adrenal medulla hormones (adrenaline, noradrenaline) and a prolonged "fight or flight" response.
Pancreatic Disorders:
Diabetes mellitus = a group of disorders caused by an inability to produce or use insulin.
Type I or insulin–dependent diabetes mellitus is caused by an absolute deficiency of insulin.
Type II or insulin–independent diabetes is caused by down-regulation of insulin receptors.
Hyperinsulinism results when too much insulin is present and causes hypoglycaemia (low blood–sugar) and possibly insulin shock.
Mechanism of Hormone action
Peptides and Amino Acid Derived hormones
Peptides and Amine hormones are non-steroidal, water soluble hormones. They are large and can't fit through plasma membrane of target cell.
Protein hormones from glands (1st messengers) do not enter the cell. They bind to receptors on plasma membrane of target cell, triggering 2nd messenger to affect cell’s activity.
Hormone receptor complex activates G–protein (Glycoproteins).
Glycoproteins generate chemical signal (2nd messenger) – most common is cAMP and IP3.
2nd messenger chemical signal activates other intracellular chemicals to produce response in target cell.
Responses may be:
- Phosphorylation.
- Activation of enzymes.
- Release of calcium ions into cytosol from Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Turn on transcription factor CREB (cyclic AMP response element–binding protein) for protein production.
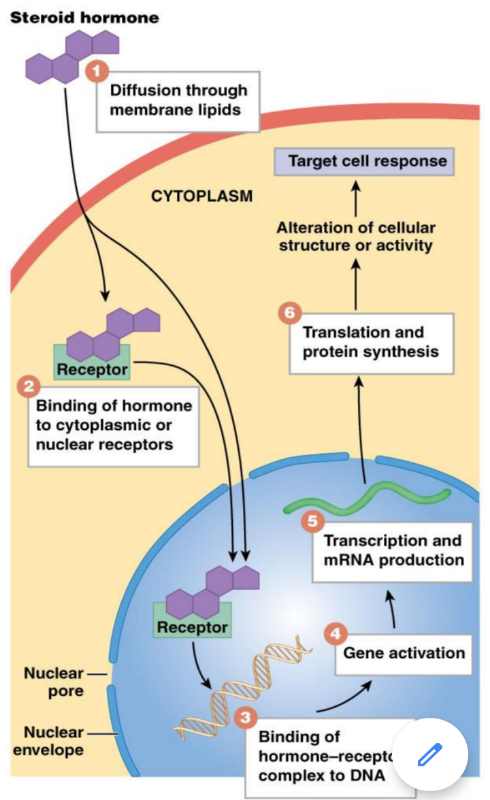
Steroid hormones
Steroid hormones are fat-soluble hormones and they bind to receptors inside target cell. They influence cell activity by acting on specific genes.
Steroid hormones diffuse freely into cell where cytoplasmic and/or nuclear proteins serve as receptors.
These hormones bind to receptor to form hormone–receptor complex.
Hormone–receptor complex acts as transcription factor to turn target genes “on” or “off”.
Summary
🍄 The Endocrine system includes all organs and tissues that produce and secrete hormones, which are used by the body to regulate and coordinate all the vital body functions.
🍄 Organs and tissues which their primary function is the production and secretion of hormones are called glands.
🍄 Exocrine glands are organs and tissues that release hormones into ducts.
🍄 Endocrine glands are glands and tissues that do not release hormones into ducts, they release hormones directly to where they are needed or into the bloodstream.
🍄 There are 3 major classes of Hormones:
- Peptide hormones
- Steroid hormones
- Amino acid-derived hormones
🍄 Peptide hormones are large protein hormones that cannot penetrate into cells, instead they bind to receptors on the wall of the cell.
🍄 Steroid hormones are lipid hormones that can penetrate into cells, and bind to receptors in the cell.
🍄 Amino acid derived hormones are gotten from simple amino acids.
🍄 Prostaglandins are lipid substances that are modified from fatty acids (arachidonic acid) and have hormone-like properties. They are a group of lipids made at sites of tissue damage or infection, and they assist during childbirth.
🍄 G–proteins/Glycoproteins activate hormonal response inside a cell.
🍄 Presence of a stimulus will lead to the production or release of a hormone, when the hormone reaches a particular level, or there's absence of the stimulus, this will lead to a halt in the production or release of the hormone, this is Negative feedback loop.
🍄 In positive feedback loop, presence of a stimulus will lead to continuous production or release of hormone. It reinforces stimulus.
🍄 The hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland through nervous stimulation (of the posterior pituitary) and hormonal secretion to the anterior pituitary.
🍄 Pituitary Gland is controlled by the hypothalamus and it secretes 9 hormones.
🍄 Thyroid gland is found in the neck region and it secretes thyroxine which regulate body metabolism.
🍄 Parathyroid glands are embedded behind the thyroid gland, and they release hormone that dissolves bone and increase Calcium level in blood.
🍄 Adrenal gland hormones control stress, salt retention, fight and flight action of the body.
🍄 Pancreatic hormones regulate blood–glucose level.
🍄 Gonadal hormones control sexual and reproductive functions in male and female animals.




















![GROUP 1A ELEMENTS [ALKALI METALS]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiTaRno3-Kj3zqgfpG848vTTt_gRDTSXvEBS97SXDiXfdr0kAAqk0taqzZFjiAMw8TLF08fqqa2CKsA70_C91Gzk9-P0YHyl8wcJfkqwtyUROMLCGmLf3GSw7c6xMFGUu9x1w8XtPemj-q662_6UoTCZOXna8YZkLzlpZVJHKer-p1EvF9eKLFNZf5pUg/w74-h74-p-k-no-nu/Group%201A%20elements%20Alkali%20metals.jpg)




